Overview
Problem Setting
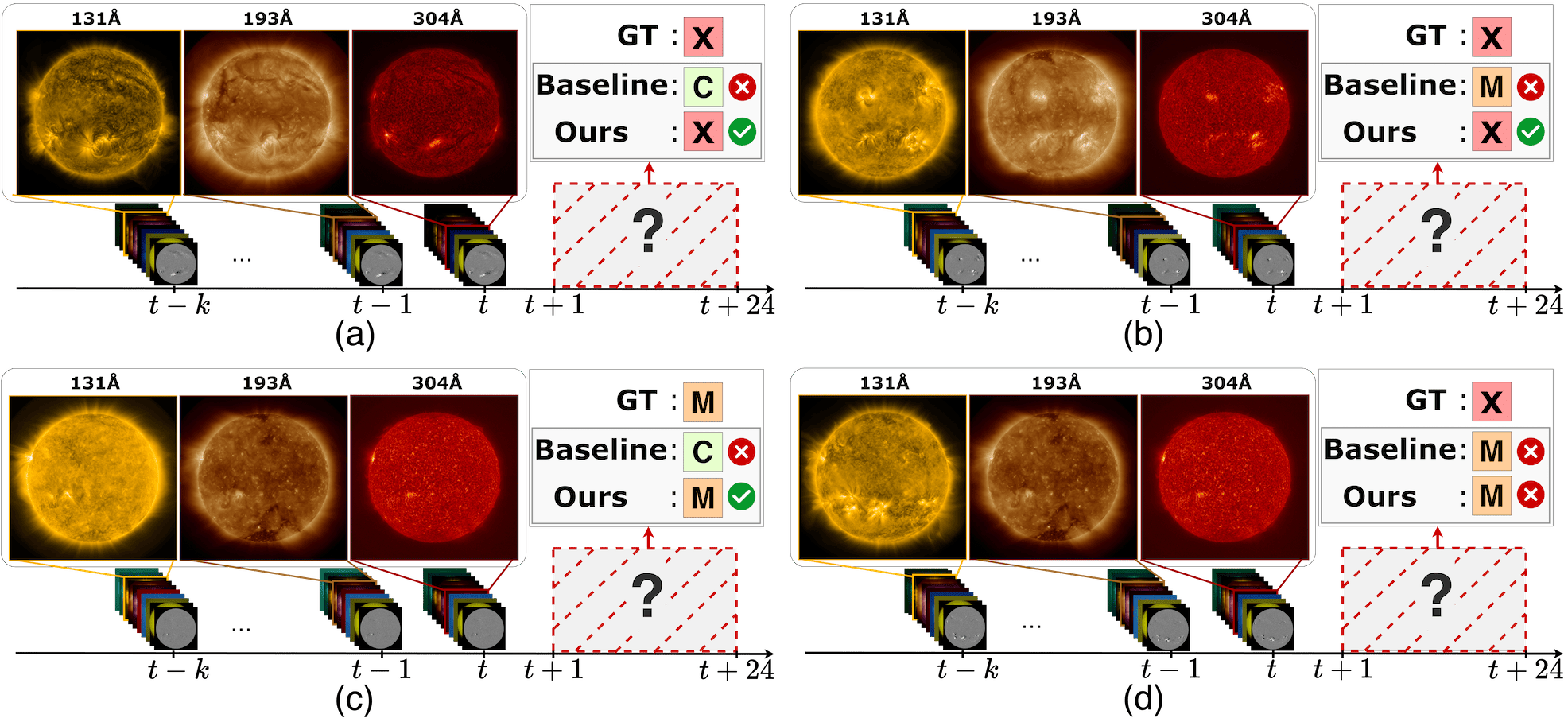
We tackle the challenging task of predicting the class of the largest solar flare within a 24-hour horizon using full-disk multi-wavelength solar images. This is formulated as a multi-class classification problem with significant real-world implications for space weather forecasting.
Correspondence between flare classes and peak X-ray flux intensities.
Model Architecture
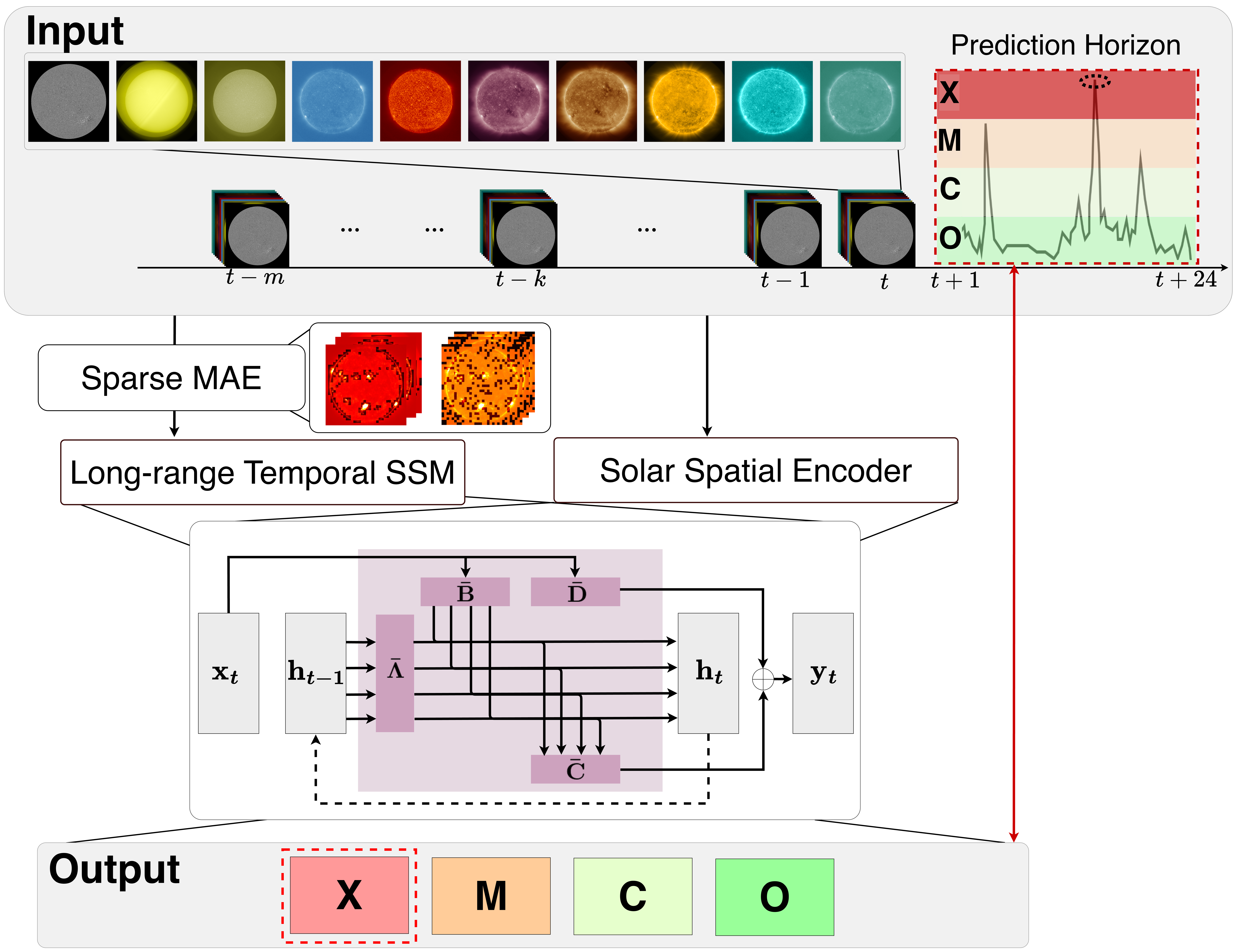
We propose Deep SWM, a novel architecture extending deep state-space models for classifying the maximum solar flare class within a 24-hour horizon, utilizing HMI and multi-wavelength AIA images.
The novelties of our proposed method are as follows:
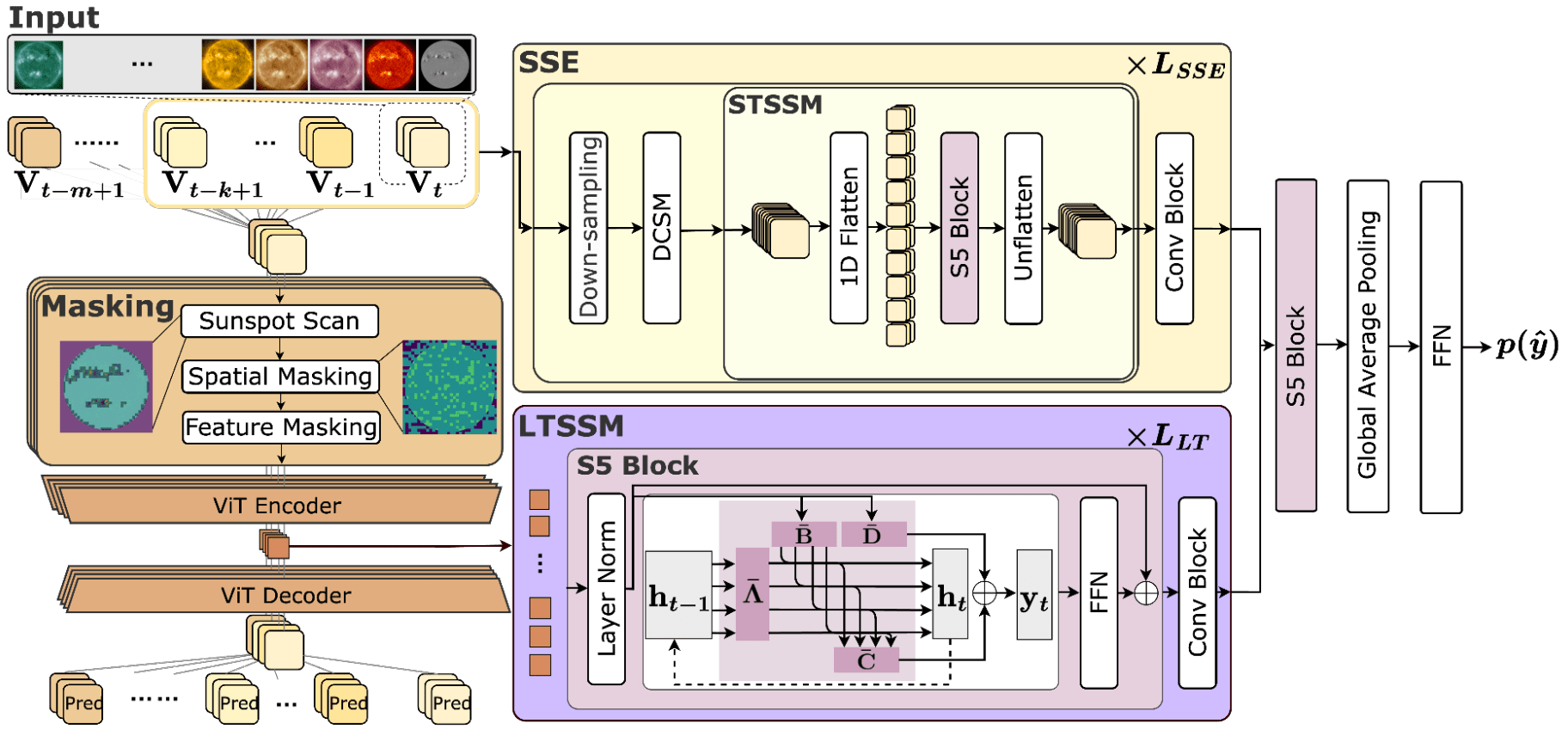
Solar Spatial Encoder (SSE)
Comprising the Depth-wise Channel Selective Module (DCSM) and the Spatio-Temporal State-Space Module (ST-SSM). The DCSM selectively weights multi-wavelength image channels to emphasize features relevant to solar events, while the ST-SSM efficiently captures long-range spatio-temporal dependencies in the solar images.
Long-range Temporal SSM (LT-SSM)
Extends deep state-space models to effectively model temporal dependencies exceeding the solar rotation period within the intermediate features obtained from the pretraining stage. This allows the LT-SSM to efficiently capture long-range relationships that are crucial for solar flare prediction.
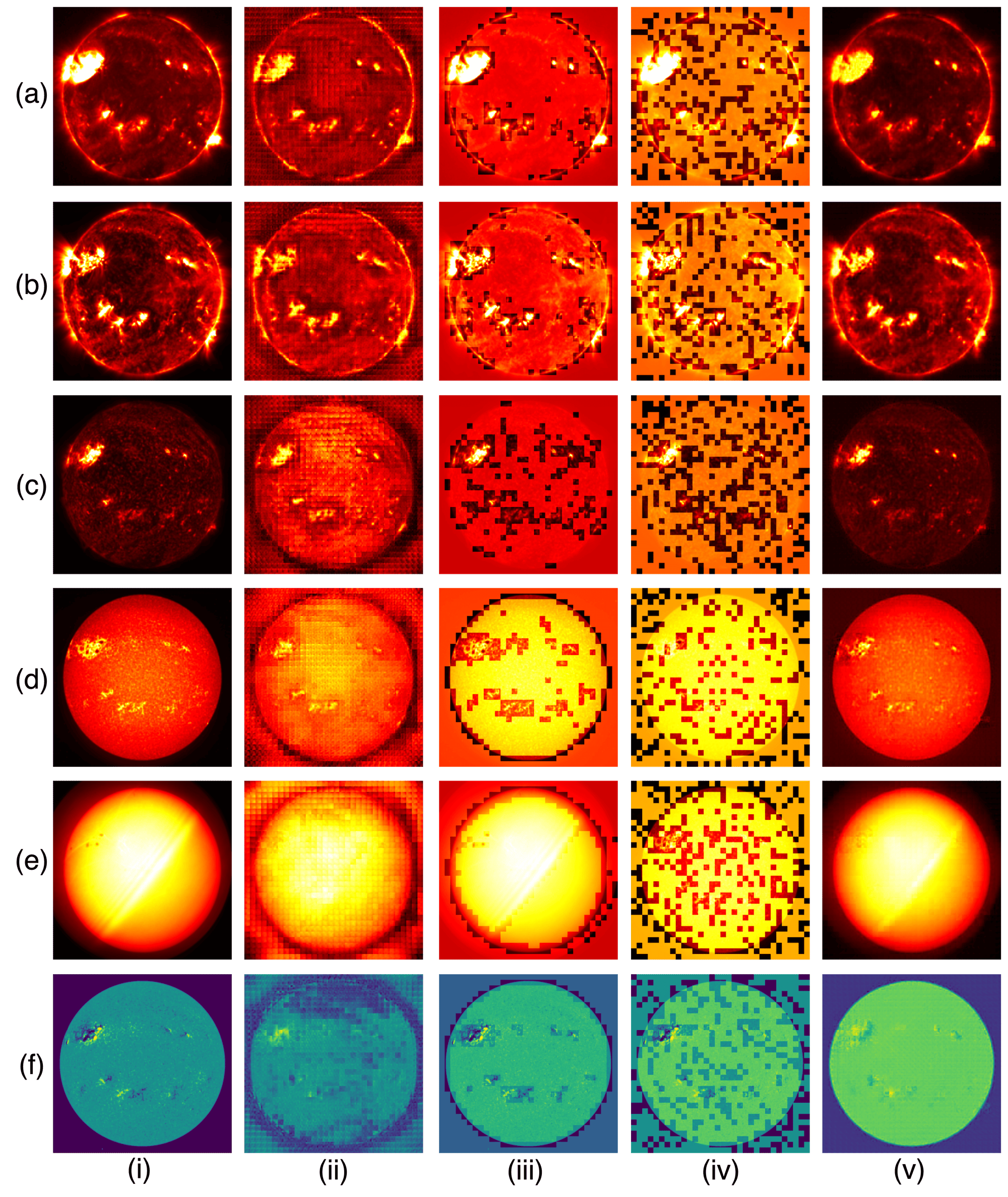
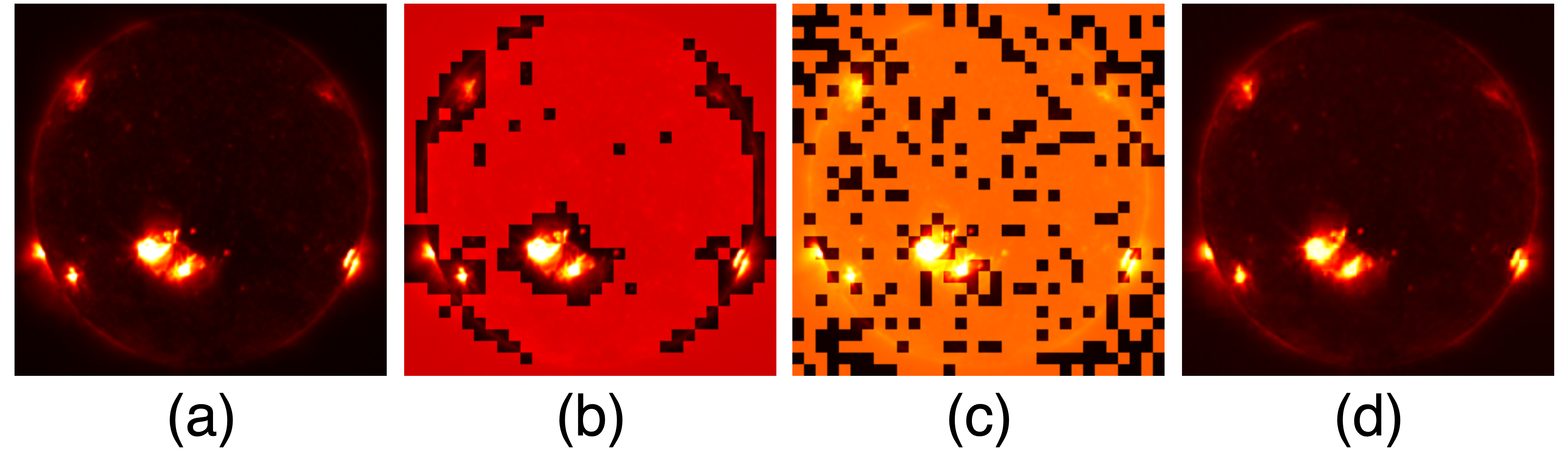
Sparse MAE
A pretraining strategy tailored for solar images that extends the Masked Autoencoder (MAE). Sparse MAE addresses the challenge of sparse, yet crucial, information regions in solar images (e.g., sunspots) using a novel two-phase masking approach. This ensures that these crucial regions are less likely to be completely masked during pretraining, leading to improved intermediate feature representations.
Quantitative Results
Our method outperforms all baseline approaches across all metrics and even surpasses human expert performance, demonstrating the effectiveness of our approach for solar flare prediction.
Table 1: Comparison of our method with state-of-the-art approaches and human experts. Higher values are better for all metrics.
Qualitative Results